Et pot interessar
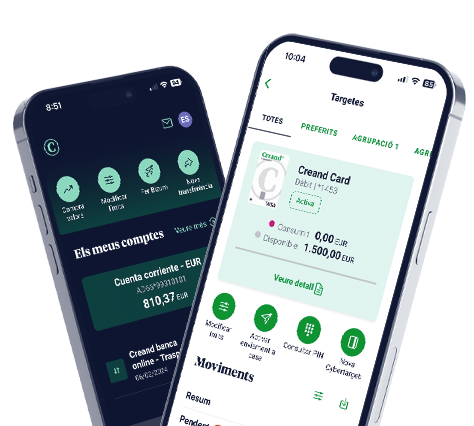
Amb Creand Banca Online, fes fàcil el que sembla difícil
Tot el que necessites per gestionar les teves finances en un sol clic amb l’opció «Operar». Configura les consultes i operacions destacades, com ara els moviments dels teus comptes i targetes, les transferències, els bizums, o l’opció de donar d’alta una cybertargeta, entre moltes altres.
Personalitza la nova app Creand Banca Online i tria la vista de la pantalla d’inici que s’adapti millor a les teves necessitats, selecciona els teus preferits i, si t’ho estimes més, passa’t al costat obscur i activa el mode fosc!
Decideix què vols rebre i quan ho vols rebre per no perdre el detall dels teus comptes i tenir-los sota control.
Interactua de manera còmoda i confidencial amb el teu gestor a través de l’app o sol·licita una cita amb ell, telefònica o presencial.
Activa la biometria per validar d’una manera senzilla totes les teves operacions de Creand Banca Online amb les notificacions push i el rostre o l’empremta.